NASA’s Newest Space Telescope
by Penelope Moroneso
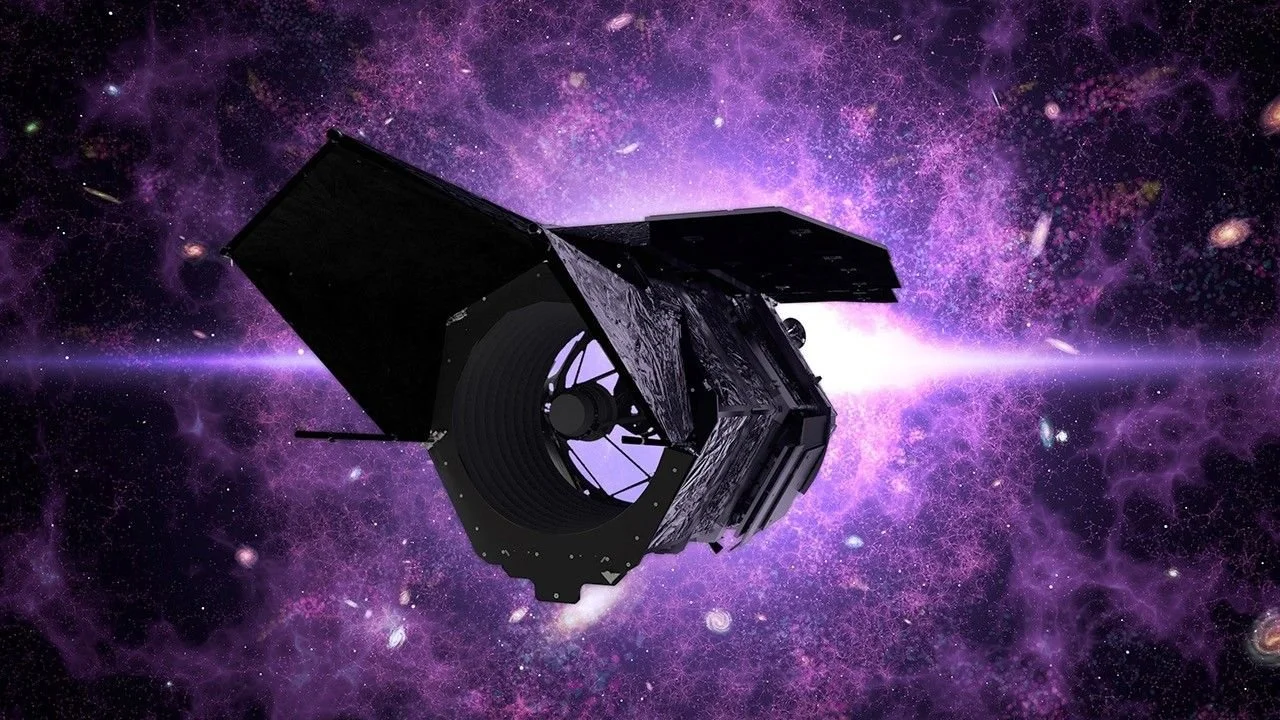
NASA is working on a new telescope, one that will outpace even the James Webb. While we’ve obtained a wealth of knowledge from previous instruments, this new telescope will have updated systems and newer cameras, hopefully adding to the collection of amazing space photographs taken by Hubble and Webb. The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is named after the first female Chief of Astronomy at NASA and one of the top contributors to the Hubble telescope’s construction. Its mission is to investigate dark matter, dark energy, exoplanets, and other mysteries of the universe. Roman will have two hundred times the range of Hubble, meaning it will be able to see that much more of the sky, resulting in a ten-fold improvement in collected data. Its powerful infrared vision could help us learn more about the history of the Milky Way and the wider universe. The telescope is set to launch a little more than a year from now, in May 2027, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once it launches, the Roman Space Telescope will be a huge resource for space discovery.
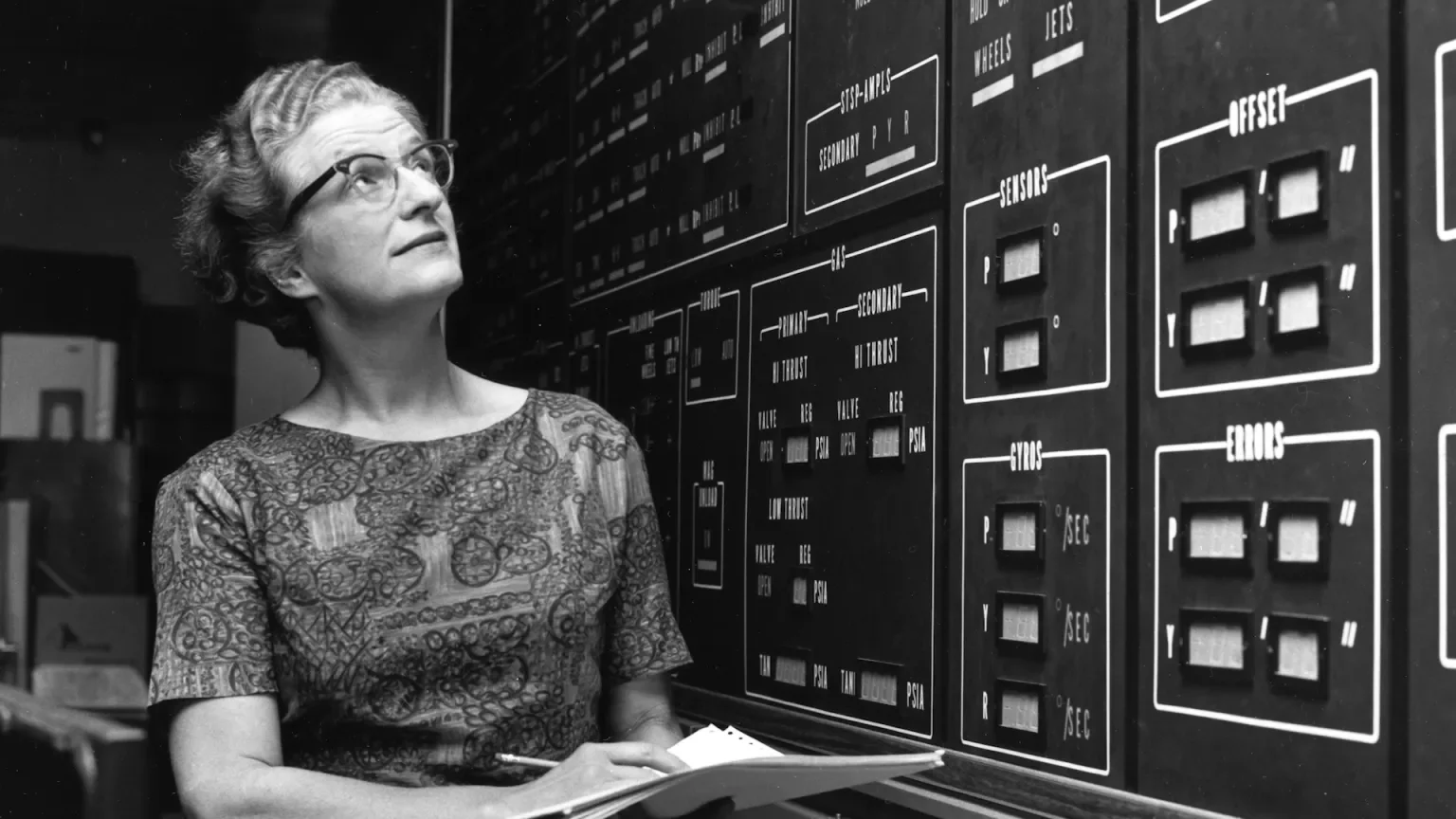
Nancy Grace Roman, shown here at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in the early 1970s, was the first female Chief of Astronomy at NASA, and through her work getting the Hubble Space Telescope approved by Congress, she earned the title "the mother of Hubble."
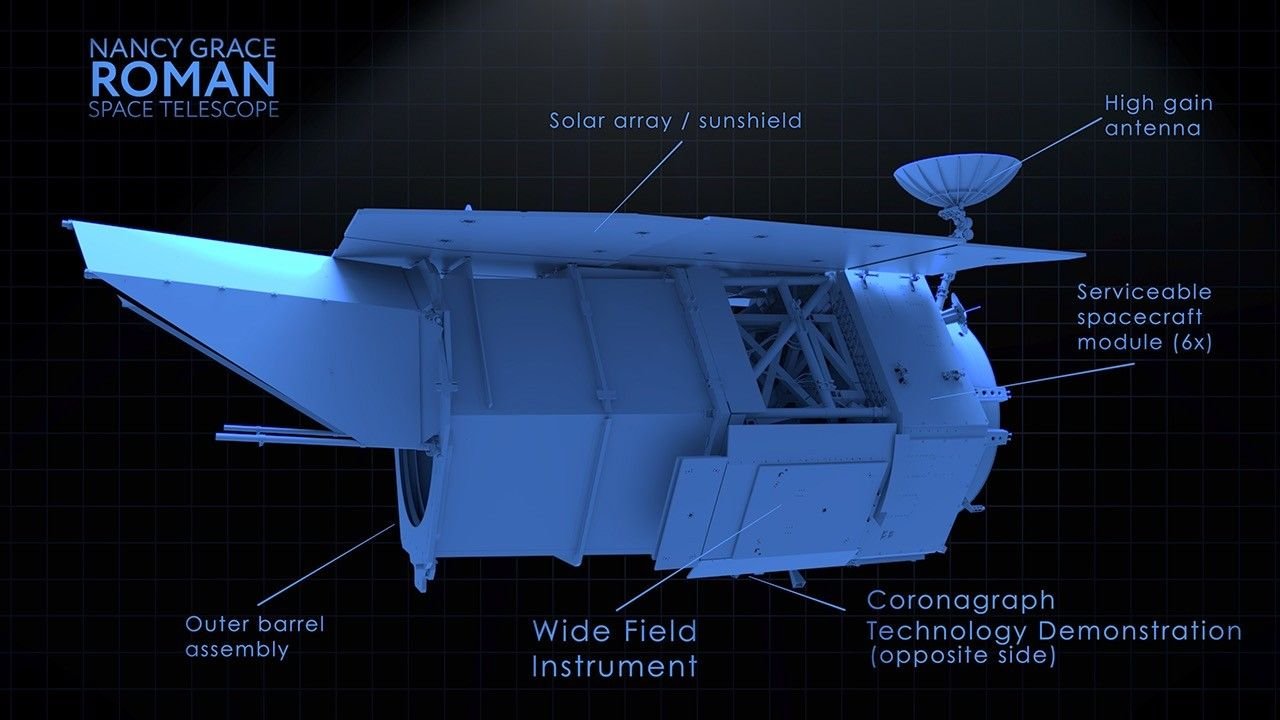
One of the main reasons the Roman telescope will be so influential is its technology and instruments. One instrument is its infrared telescope, also called NASA’s Wide Field Instrument. According to the article NASA Roman Core Survey Will Trace Cosmic Expansion Over Time from nasa.gov, the telescope “will capture an area 200 times larger than the Hubble Space Telescope’s infrared camera, and with the same image sharpness and sensitivity.” The instrument will be used to conduct a survey looking for type Ia supernovae, which always go supernova at the exact same mass and therefore are the same brightness. This survey will help scientists better understand how the universe has expanded over time. Since this type of supernova always has equal brightness, we can use them to measure large distances with the Inverse Square Law. Another tool the telescope has is a coronagraph, which will aid another important mission: the discovery of exoplanets. A coronagraph is a complex system of masks, detectors, prisms, and flexible mirrors that can block the light from distant stars in order to directly image any planets orbiting them. As NASA explains on its website, the new telescope’s coronagraph will be two to three orders of magnitude more powerful than any other coronagraph on-board current space telescopes. This better technology could also bring us clearer images of very young star systems and enable us to discover more about how solar systems, including our own, form.
The tremendous amount of information that this telescope could gather is also important. As previously stated, Roman’s infrared telescope will observe how the universe has been expanding since its conception during the Big Bang, and it will also make significant contributions to the study of dark energy, as dark energy is the suspected cause of this expansion. A project named the Dark Energy Survey has shown that dark energy might be slowly weakening over time, and Roman could help astronomers test this theory. In addition, according to the CalTech website, this telescope’s large view will allow us to map four times as many stars in our galaxy as we already have. Although scientists know what the Milky Way looks like from observing other spiral galaxies, they don’t have a complete picture. One reason for that is that dust clouds can block our sight, like a fog. However, infrared has less trouble passing through this “fog,” so Roman will be able to see much farther. We may even glimpse clues to how our planet and solar system formed, by using the wavelengths of light to detect the composition of the dust.
In conclusion, the new Nancy Roman Grace space telescope and its revolutionary technology will help bring about many new discoveries in the field of astronomy. Its infrared telescope can detect supernovae billions of light-years away and pierce through clouds of dust, helping us understand the origins of our universe and our own planet. Its coronagraph will be used to find and photograph other worlds like ours, and add even more to the picture of how Earth came to be. Much like its predecessors, this space telescope will undoubtedly usher in a new era of scientific discovery.
Interested in learning more? Check out NASA’s website on the Roman project and its future mission here